As the previous article about Power Users in a Self-Service BI Initiative discussed, there are multiple types of Self-Service BI with varying needs, abilities, and preferences. The Microsoft ecosystem has many capabilities for the creation of reports and dashboards, data models, data integration and cleansing, statistical analysis, predictive analytics, as well as analysis of geospatial, unstructured, and streaming data.
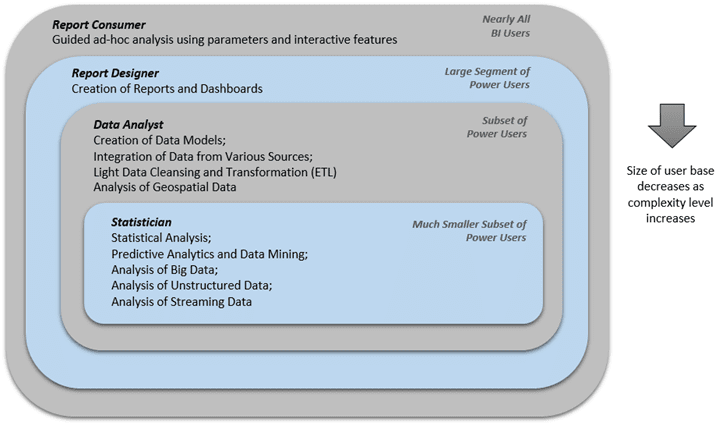
Although different organizations will use terms different ways, the following image offers one way to categorize the types of Self-Service BI users:
To build on that idea, the following table translates our different types of Self-Service BI users to the Microsoft tools they are likely to use and for what purpose. Note this table includes traditional Self-Service BI tools, plus a number of capabilities which are not commonly thought of in this manner.
For additional relevance and comparison to the above, the following table lists Corporate BI tools as well.
Level of Infrastructure Investment for Self-Service BI May Vary Significantly
The table above lists many types of diverse capabilities in the Microsoft ecosystem which can be used to support Self-Service BI. Some require minimal technical investment, whereas others require management of back-end systems by IT professionals and/or custom development work. For example, sharing and refreshing Power Pivot models in SharePoint is a pretty straightforward process for functional users to perform, but it does require technical staff to install, configure, and maintain the infrastructure behind it.
On-Premises vs. Cloud vs. Hybrid
Traditionally, Self-Service BI tools have been managed on-premises in which the organization bears responsibility for installing and configuring the hardware, software, and networking components. Cloud-based systems, such as Power BI for Office 365 (which includes Power Pivot, Power Query, Power View, and Power Map), are emerging as a trend which minimizes the investment in infrastructure and offers new features at a faster pace. Some organizations are finding themselves considering a hybrid BI model with some functionality being delivered on-premises and some via cloud-based systems.
Conclusion
There are many capabilities available in Office, Office 365, Azure, SQL Server, and SharePoint that your organization can take advantage of in order to support the needs, abilities, and preferences of various power users. As capabilities continue to evolve that put tools into the hands of information workers that are easier and easier to use, we expect to see Self-Service BI continue to grow and complement Corporate BI for reporting and analytics.